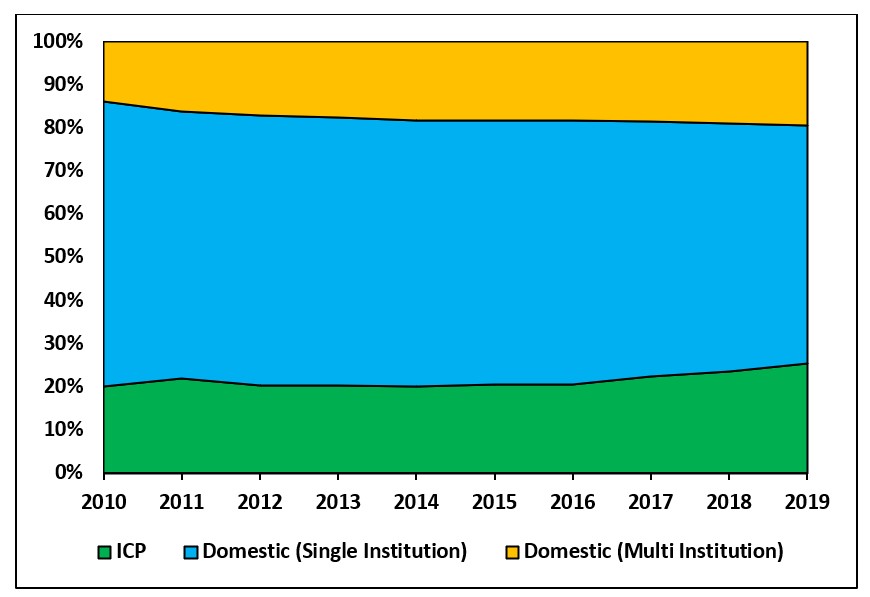
International Collaboration Patterns
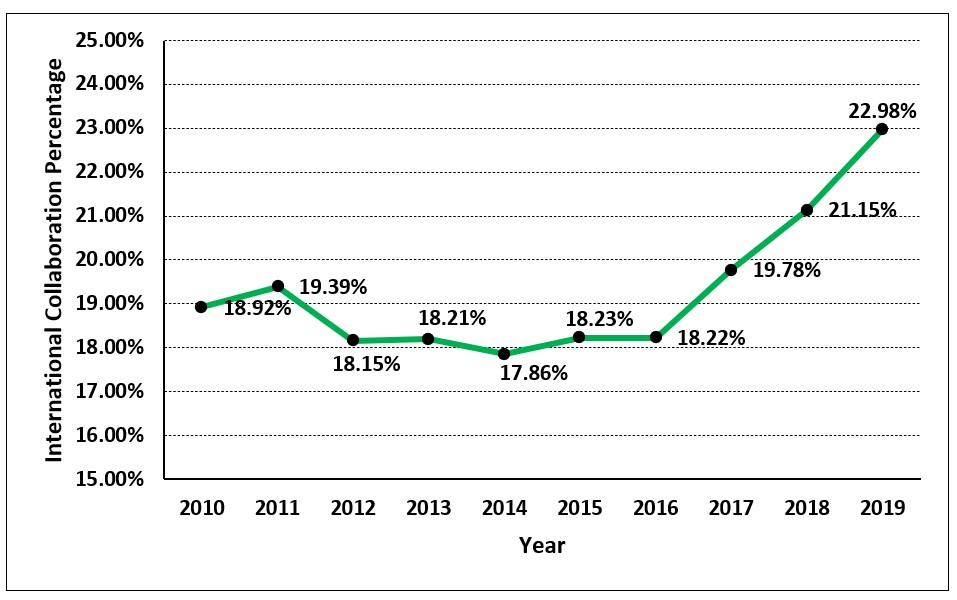
India's international collaboration networks seem to have improved during 2010 to 2019. In 2010, a total of
18.92% of India's research output involved international collaboration which has grown to 22.98%
of the total research output in 2019. Since 2016, the growth in international collaboration is more steep. The figure below
shows the percentage share of internationally collaborated papers in India's research output.
The amount of internationally collaborated papers from India are, however, lesser as compared to the 20
major countries. For example, United Kingdom has 48.73% of it's research output that involves international
collaboration. Similarly, France has 50.43%, Australia has 50.98%, and Switzerland has 65.63% of it's research
output, during 2010 to 2019, involving international collaboration. The table below shows international collaboration
patterns of the 20 major countries considered.
| Rank |
Country |
TP (2010-2019) |
ICP (2010-2019) |
ICP (%) |
| 1 |
United States |
6,181,247 |
1,959,644 |
31.70 |
| 2 |
China |
3,828,795 |
883,947 |
23.09 |
| 3 |
United Kingdom |
1,824,427 |
889,118 |
48.73 |
| 4 |
Japan |
1,694,585 |
344,508 |
20.33 |
| 5 |
Germany |
1,551,543 |
732,467 |
47.21 |
| 6 |
France |
1,103,707 |
556,554 |
50.43 |
| 7 |
India |
1,084,422 |
211,740 |
19.53 |
| 8 |
Canada |
970,336 |
460,453 |
47.45 |
| 9 |
Italy |
936,918 |
423,813 |
45.23 |
| 10 |
Australia |
840,791 |
428,650 |
50.98 |
| 11 |
Spain |
825,399 |
365,192 |
44.24 |
| 12 |
Brazil |
791,088 |
202,983 |
25.66 |
| 13 |
South Korea |
714,331 |
192,027 |
26.88 |
| 14 |
Russia |
616,395 |
160,458 |
26.03 |
| 15 |
Netherlands |
548,489 |
308,024 |
56.16 |
| 16 |
Switzerland |
417,766 |
274,177 |
65.63 |
| 17 |
Iran |
401,528 |
91,611 |
22.82 |
| 18 |
Poland |
364,627 |
116,614 |
31.98 |
| 19 |
Sweden |
354,801 |
215,648 |
60.78 |
| 20 |
Taiwan |
351,371 |
101,556 |
28.9 |
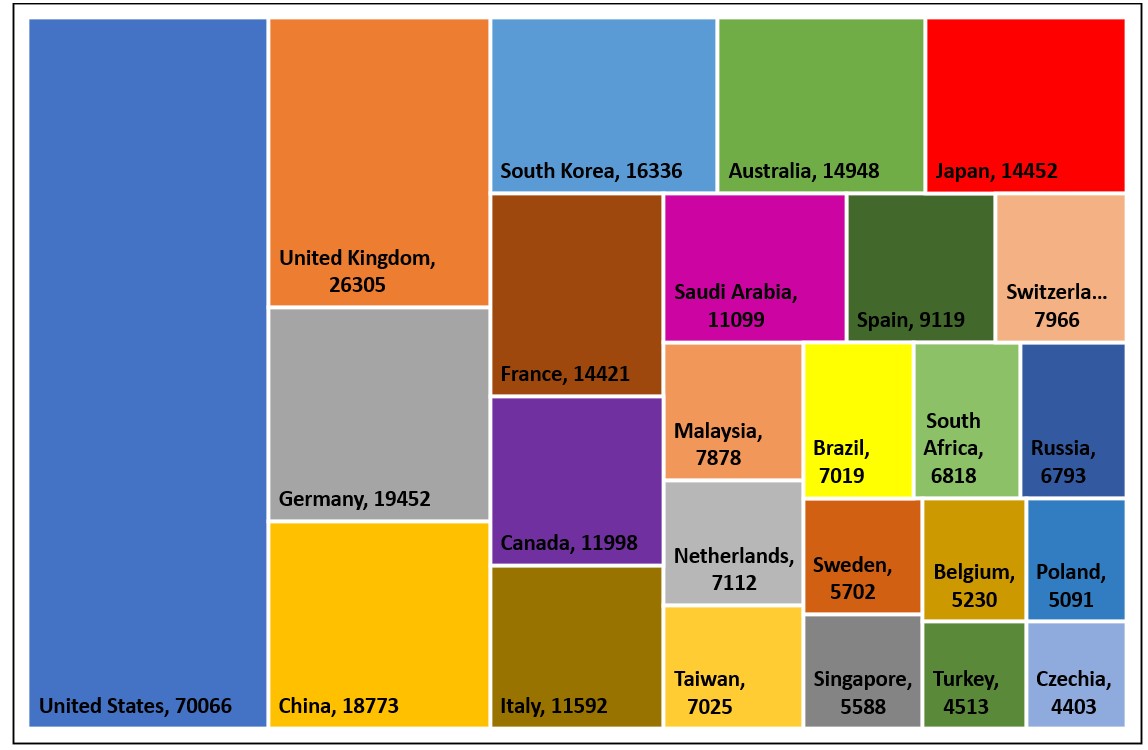
India's major collaborating partner countries
India's major collaborating partner countries during 2010 to 2019 includes -
United States of America (33.09%),
United Kingdom (12.42%),
Germany (9.19%),
China (8.87%),
South Korea (7.72%) and Australia (7.06%).
The figure below shows a list of top 25 collaborating partner countries along with the number of collaborated
papers during 2010 to 2019.
Subject area-wise distribution of domestic and Internationally Collaborated papers
The international collaboration patterns in Indian research output vary across different subject areas. It ranges from
a low of 15.88% in Language, Communication and Culture to 32.55% in Earth Sciences. Subject areas with relatively higher international
collaboration percentage are Physical Sciences (31.67%), Economics (29.44%), Built-Environment and Design (28.72%),
Environmental Sciences (28.69%). The domestic multi-institution collaborated output varies across different subject areas.
For example, Earth Sciences has 24.87% research output as multi-institution collaboration, whereas History and Archeology has only
6.68% of it;s research output involving domestic multi-institutional collaboration. The figure below presents the
subject area-wise distribution of domestic and internationally collaborated research output of India.
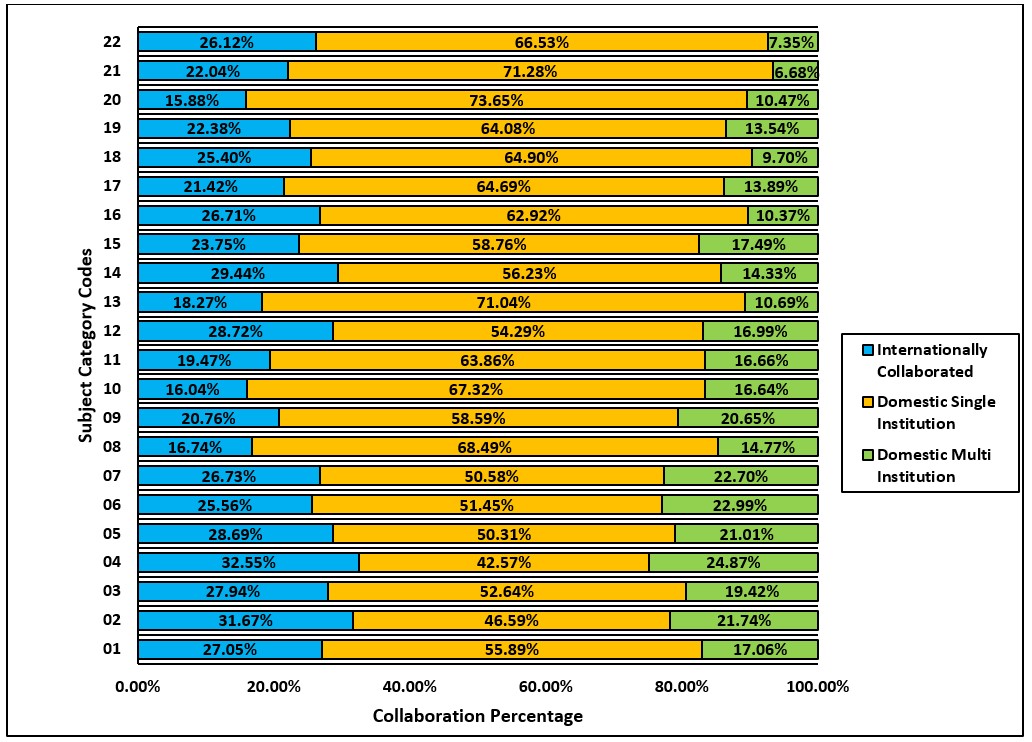
**Subject Codes - 01-Mathematical Science, 02-Physical Sciences, 03-Chemical Sciences, 04-Earth Sciences, 05-Environmental Sciences,
06-Biological Sciences, 07-Agricultural and Veterinary Sciences, 08-Information and Computing Sciences, 09-Engineering,
10-Technology, 11-Medical and Health Sciences, 12-Built Environment and Design, 13-Education, 14-Economics,
15-Commerce, Management, Tourism and Services, 16-Studies in Human Society, 17-Psychology and Cognitive Sciences,
18-Law and Legal Studies, 19-Studies in Creative Arts and Writing, 20-Language, Communication and Culture,
21-History and Archaeology, 22-Philosophy and Religious Studies
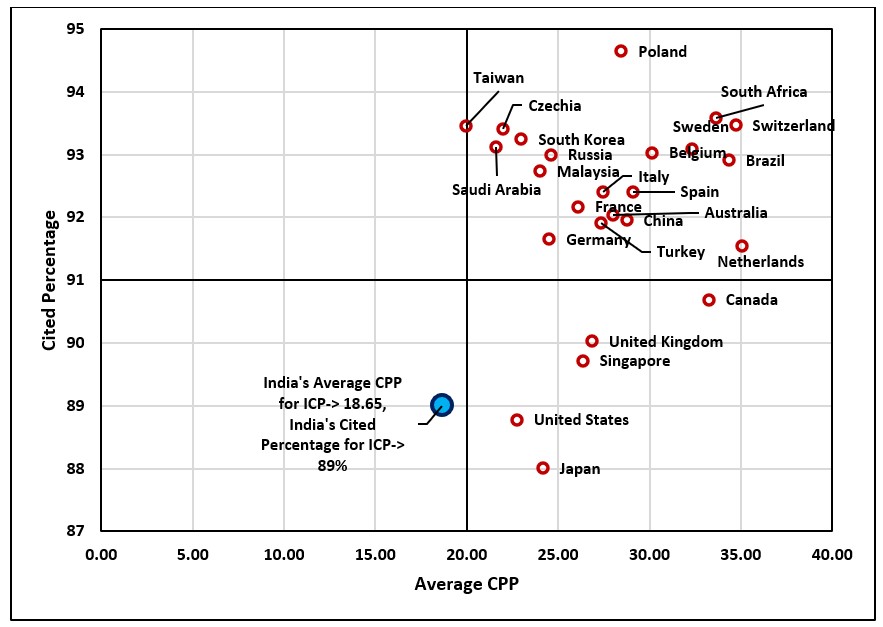
Citation impact of Internationally Collaborated Papers
The International Collaboration seems to have an advantage in terms of citation impact as compared to domestic papers.
For example, the average citations per paper (ACPP) for domestic papers is 7.95, whereas the average citation per paper
for Internationally Collaborated papers is 18.65. Similarly, the cited percentage of domestic papers is 76.75%
whereas for internationally collaborated papers, it is 89%. Further, International Collaboration with different
countries shows different impact, as shown in the figure below. For example, collaboration with Switzerland leads to a
cited percentage of more than 93%, with an ACPP of 35. On the other hand, collaboration with Japan has a cited
percentage of 88%, with an ACPP value of 24.5.